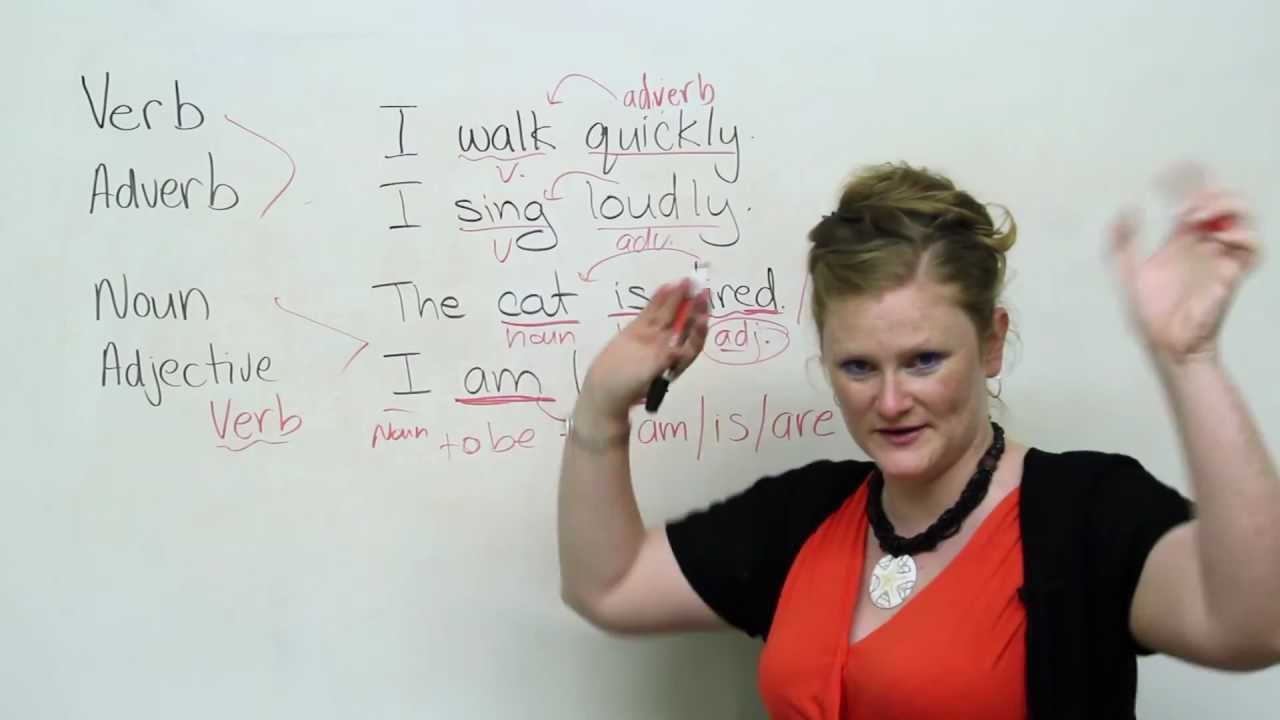Wednesday, January 12, 2022
Wednesday, January 5, 2022
What Is The To Be Verb In English
The verb "to be" in English has a different form in the present, past, and future tenses. The present tense forms are "am", "are", and "is", depending on the pronoun. The past forms are "was" and "were", also depending on the pronoun, while the future tense uses the verb "will" before "be".
We can also mention the past participle form "been" that is used in all perfect tenses, as well as the passive. The opposite of a transitive verb is an intransitive verb. A verb is an intransitive verb if it is not used with a direct object. Remember, only nouns, pronouns, and noun phrases can be direct objects. Prepositional phrases, adjectives, and adverbs cannot be used as direct objects.
Once again, both action and stative verbs can be used as intransitive verbs. "To be" verbs change almost more than any other verb. Let's learn how to use "to be" verbs correctly. Refer back to this lesson when you have questions about how to use them in the future. While the prepositional phrases here give important information and context, they are not direct objects.
To-be forms are considered intransitive linking verbs, and could not be included in sentences with reflexive verbs. The verbs do, say and have additionally have irregular third person singular present tense forms . The copular verb be is highly irregular, with the forms be, am, is, are, was, were, been and being. On the other hand, modal verbs are defective verbs, being used only in a limited number of forms. For details on the forms of verbs of these types, see § Copular, auxiliary and defective verbs below.
In these constructions, the "to be" verb will follow the standard rules for subject verb agreement. The examples below have sentences using "to be" verbs in different tenses. In the example sentence, she applied herself means that the woman gave her full attention to the job she was doing. In addition to having the meaning change, there are times where you don't need to include a pronoun.
This is usually the case when the action implies that the subject and the object are the same. Transitive VerbsTransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities that relate or affect someone or something else. In a sentence with a transitive verb, someone or something receives the action of the verb. The past participle is used for the perfect tenses. In regular verbs, it's the same as the simple past tense, so there's nothing extra to learn.
However, irregular verbs often use unique past participles, so you may have to memorize their forms. Now you understand the two things to look for to identify reflexive verbs in standard reflexive verbs English use. A reflexive verb can be any action word, if the word is transitive, and it's next to a reflexive pronoun. Reflexive pronouns are connected to subjective pronouns.
The action actually reflects back to the subject through the suffix of self to show the performer of the action is also the receiver of the action. The pronoun that you select depends on who the subject is that's performing a certain action. Auxiliary verbs are also known as helping verbs and are used together with a main verb to show the verb's tense or to form a question or negative. Common examples of auxiliary verbs include have, might, will. These auxiliary verbs give some context to the main verb, for example, letting the reader know when the action took place. In our regular Grammar 101 series, we look at commonly confused words like"its" vs "it's".
Verb tenses inform us how an action relates to time and can create a lot of confusion if used incorrectly. We suggest you familiarise yourself with the different verb tenses as verbs can change forms depending on the tenses they are used in. The general rule for the past simple tense is to add "ed" at the end of the verb, but this doesn't apply to all verbs. When giving imperatives or commands, "to be" verbs stay in the base form of be and typically stay at the beginning of the sentence. In these sentences, the subject is implied so it doesn't have to be written, that is why you only see the "to be" verb followed by the complement. Next, you have taught, which is the transitive verb in this sentence.
It's the past tense of the infinitive form, to teach. This transitive form must have a direct object; it cannot stand alone in a sentence. Transitive verbs are the first requirement for a reflexive verb to exist in a given sentence.
The second requirement for reflexive verbs in standard reflexive verbs English use will be discussed later in this guide. A transitive verb is a verb that is accompanied by a direct object in a sentence. The direct object is the noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that is having something done to it by the subject of the sentence. Both action and stative verbs can have direct objects, which means they can both be used as transitive verbs. What is often called the future tense of English is formed using the auxiliary will. The simple future is will write, the future progressive is will be writing, the future perfect is will have written, and the future perfect progressive is will have been writing.
Traditionally shall is used rather than will in the first person singular and plural; see shall and will. These verbs are can and could, may and might, shall and should, will and would, as well as must, ought , need and dare , and in some analyses used and had better. The negation of can is spelled as a single word, cannot. There are contracted forms 'll and 'd for will and would . A regular verb forms its verb tenses, especially thepast tenseandpast participle, by adding one in the set of generally accepted standardized suffixes.
Regular verbs are conjugated by adding -d, -ed, -ing, or -s to its base form, unlike irregular verbs which have special rules for conjugation. They do not work as verbs in the sentence rather they work as nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc. Non-finite verbs do not change according to the number/person of the subject because these verbs, also called verbals, do not have any direct relation to the subject.
Sometimes they become the subject themselves. Auxiliary verbs, or "helping verbs," are used in English to change another verb's tense, voice, or mood. When auxiliary verbs are used, there's always a main verb that represents the main action.
However, the auxiliary verb must still be conjugated correctly. No direct object is necessary to form a complete sentence, making agreed an intransitive word, and therefore, not included in standard reflexive verbs usage. Words that are only intransitive cannot be in a reflexive verb sentence. Remember, a transitive sentence will always have a direct object, allowing it to meet the first requirement of being a reflexive verb in standard reflexive verbs English use.
Auxiliary use - You can only use modal verbs as auxiliary verbs, in order to modify the meaning of the main verb. Intransitive verbs are action verbs that always express doable activities. They are different from transitive verbs because there is no direct object following an intransitive verb. Helping verbs, also called auxiliary verbs, are helpful verbs that work with other verbs to change the meaning of a sentence. A helping verb combines with a main verb in order to accomplish different goals.
These include changing the tense of the verb or altering the mood of a sentence. Unlike action verbs, stative verbs refer to conditions or states of being. Generally speaking, we use stative verbs to describe things like qualities, states of existence, opinions, beliefs, and emotions. When used in a sentence, stative verbs do not refer to actions. It is important to know that some verbs can be used as either action or stative verbs depending on their meaning in the sentence.
We are less likely to use stative verbs in the continuous verb tenses. For the next little while, we're going to focus on main verbs. So, forget about those poor little helping verbs for a bit, and let's turn our attention to action verbs and linking verbs. These two kinds of main verbs can act in four different ways. When used with the present participle of other verbs it describes actions that are or were still continuing - auxiliary verb be [+ ing form of the main verb]. Most irregular verbs have three principal parts, since the simple past and past participle are unpredictable.
For example, the verb write has the principal parts write , wrote , and written ; the remaining inflected forms are derived regularly from the base form. Note that some irregular verbs have identical past tense and past participle forms , as with send–sent–sent. The copula verb be has a larger number of different inflected forms, and is highly irregular. Some verbs in this list can also be action verbs. To figure out if they are linking verbs, you should try replacing them with forms of the be verbs.
If the changed sentence makes sense, that verb is a linking verb. The linking "to be" verb describes the condition of the subject. Below are a few sentence structures using the linking "to be" verbs.
The previous section contained examples of what most beginners need to learn for using "to be" verbs correctly. In this section, we'll be covering many other ways to use them. The correct "to be" verb to use depends on your subject and tense. This chart shows you proper subject verb agreement with "to be" verbs.
Modals or Modal Verbs or Modal Auxiliary are used to show the mood or attitude of the subject. They are the verbs that are used to indicate modality. Such as likelihood, ability, permission, request, capacity, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice. Modal verbs always accompany the base form of another verb having semantic content. Modals are the type of auxiliary expressing the subject's mood.
They give information about the function of the main verb. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are can, could, may, might, must, will, would, shall, should, ought to, had better, "have to" and sometimes need or dare. The three verbals— gerunds, infinitives, and participles—are formed from verbs, but are never used alone as action words in sentences.
Instead, verbals function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. As a main verb, the verb "to be" acts as a linking verb. Linking verbs are a special type of stative verb whose name gives a big clue as to what they do. Linking verbs are used to link a subject with a subject complement. A subject complement describes or identifies the subject of the sentence or clause. Linking verbs can function as intransitive verbs, which do not take direct objects.
When we write sentences or clauses, we need to include a verb. A verb is a word that we use to refer to actions and states of being . For example, the words describe, eat, and rotate are verbs.
As you are about to see, verbs come in a lot of different types that don't all behave the same way. When using proper grammar, it is important that you use verbs correctly. So, we are going to explore the many different types of verbs that we use and how to successfully use them to create great, clear sentences.
Apart from the simple past tense described above, English verbs do not have synthetic forms for particular tenses, aspects or moods. For the usage of these forms, see § Use of verb forms below. More detail can be found in the article Uses of English verb forms. Verbs constitute one of the main parts of speech in the English language.
Like other types of words in the language, English verbs are not heavily inflected. Most combinations of tense, aspect, mood and voice are expressed periphrastically, using constructions with auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs.
An auxiliary verb extends the main verb by helping to show time, tense, and possibility. The auxiliary verbs are – be verbs, have, and do. The "to be" verb used in the question tag must be the same one used in the statement. This is the form of the "to be" verb used with the perfect and passive tenses, and it is the same for all the subjects. When learning English you need to know the meaning of certain words first, and then sort the words appropriately according togrammaticalrules. Verbs in a regular structure can be transformed with a simple rule, whereas in irregular verbs, this situation is slightly different.
It may be a good start to make somememorizationand learn how to use the verbs in the right places. In all the above examples, the action is to introduce. Because it's a transitive word next to a pronoun, it reflects usual reflexive verbs usage in a sentence. But what about when the word introduce doesn't follow a reflexive pronoun, like in the sentence Jake introduces his dog to the class?
Access Control Allow Origin Nodejs Express
To repair this and to permit statistics to move between your server and client, you possibly can actually add CORS help to your server. The ...

-
To repair this and to permit statistics to move between your server and client, you possibly can actually add CORS help to your server. The ...
-
The verb "to be" in English has a different form in the present, past, and future tenses. The present tense forms are "am...
-
Empty Message